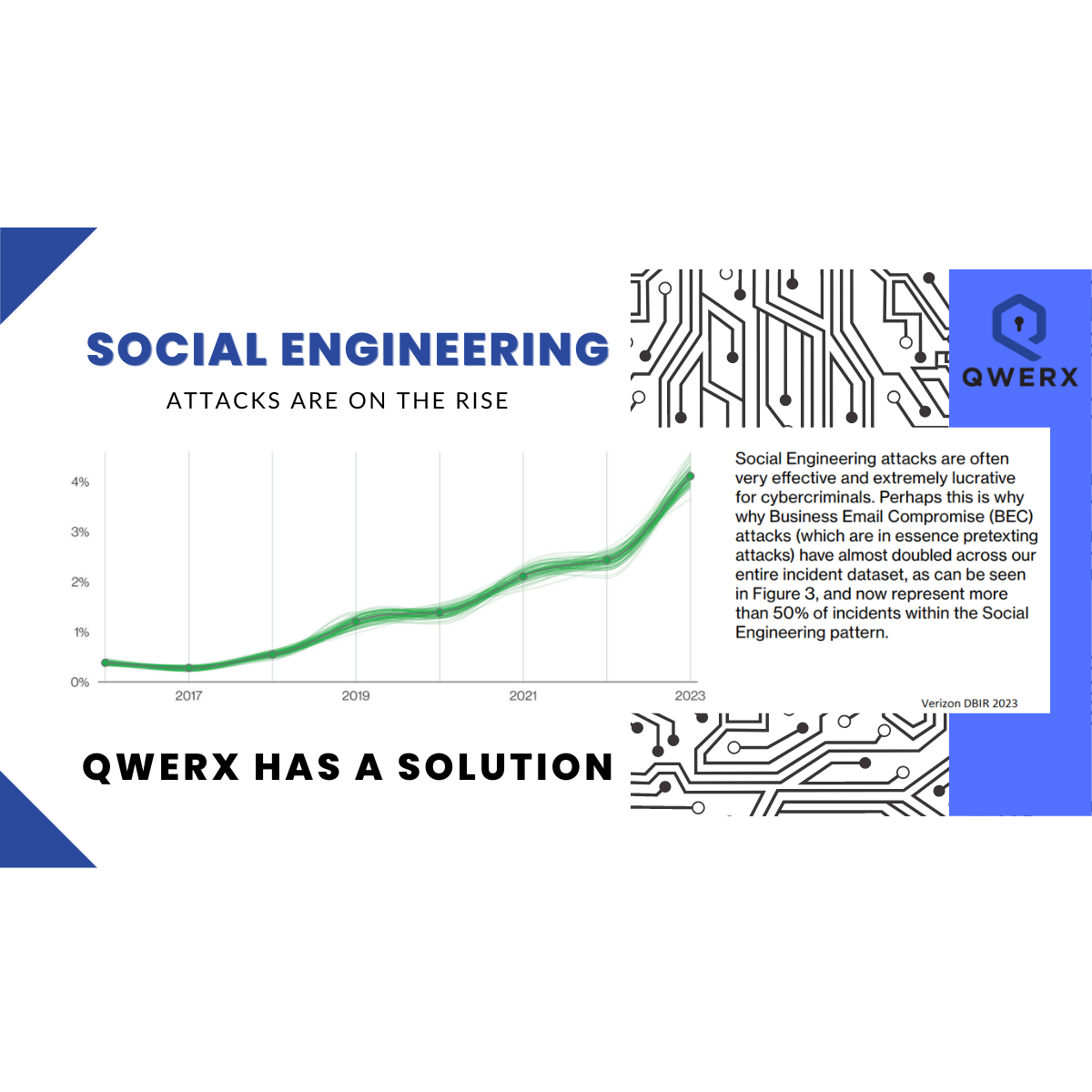
How QWERX Addresses Distributed Ledger and Blockchain Cybersecurity

Contrary to popular belief, blockchain cybersecurity isn’t invincible. The powerful technology is being widely and rapidly adopted because of its decentralization capabilities, where there isn’t a single point of failure. The distributed ledger is capable of recording and verifying a staggering number of transactions at speed, making it ideal for many industries. According to CBInsights, State of Blockchain 2021 report:
- Funding to blockchain upstarts grew from $3.1 billion in 2020 to $25.5 billion in 2021.
- An increase of 713% year-over-year.
- NFT (non-fungible token) startup funding grew from $37 million in 2020 to $4.8 billion in 2021.
- An increase of 12,878% year-over-year.
Blockchain cybersecurity can now be found in more and more industries, including financial services, infrastructure and energy, hedge funds, accounting, insurance, law enforcement and even charitable giving. Thus, it’s more critical than ever to understand the inherent risks of blockchain cybersecurity.
What Is Blockchain Cybersecurity?
A blockchain is a distributed ledger with countless (typically millions) of users across a worldwide network. All of the data within the blockchain is verified by each user, as well as any subsequent data added to the blockchain.
Blockchain cybersecurity benefits from this inherently decentralized public ledger via data transparency and multiple points of verification. There are three main keys to blockchain security:
- Decentralization. There is no one single point of failure.
- Transparency. All transactions are visible by every user on the network. Each user is protected by a unique alphanumeric address identifier. This anonymity (pseudonymity) allows transactions to transpire on the network and simultaneously provides a high degree of privacy.
- Immutability. Every transaction that is added to the blockchain cannot be altered because it is interconnected with every preceding transaction record.
The Challenges of Blockchain Cybersecurity
Blockchain cybersecurity networks are still subject to cyberattacks and fraud risks.
Code Exploitation
According to IBM, through code exploitation, more than $60 million of Ethereum (digital currency) was stolen from The Decentralized Autonomous Organization (DAO), a venture capital fund.
Blockchain Bridge Hacks
In March 2022, around $615 million in USDC and Ethereum was stolen from the Axie Infinity’s Ronin Network after hackers used hacked private keys to forge fake withdrawals. Many crypto owners used multiple blockchain networks. For convenience, Ronin developers created the Ronin bridge, connecting Axie Infinity to popular blockchains. Ronin said, “the breach resulted in 173,600 Ethereum and 25.5 million USDC being drained from the Ronin bridge in two transactions.”
Bad State Actors
State-level-backed hacker groups such as Lazarus Group, an elite North Korea-linked hacking group, are estimated to have stolen roughly $1 billion of cryptocurrency from DeFi protocols.
1% Attacks
When an organization or individual aggregates more than half of the hash rate, they can seize control of the entire system. The order of transactions can then be modified and even be reversed from previously completed transactions.
Phishing Attacks
Hackers send seemingly legitimate emails with fake hyperlinks or attachments designed to steal the user’s credentials.
Routing Attacks
Blockchain users are often unaware of the threat because hackers use the account’s anonymity to steal data as it is being transmitted to internet service providers.
The QWERX Advantage
The QWERX patented method offers significant protection for the previously mentioned catastrophic scenarios. In contrast to PKI (public key infrastructure), QWERX uses symmetric keys that are not ever exchanged or retained. Furthermore, QWERX technology doesn’t rely on standard credentials. They are dynamic. And even if stolen, they become ineffective after a very short time window.
Pervasive cybersecurity challenges like phishing attacks, stolen keys and code exploitation are rendered effectively useless because:
- The keys are generated using chaotic information and are quantum proof. Even a quantum computer can’t guess them.
- The keys are dynamic, frequently updated and not an exchange of keys.
- It doesn’t rely on mathematical processing, so it’s less burdensome on the network.
- There are no static credentials to steal — because the credentials are ephemeral.
If QWERX and Blockchain Cybersecurity Had a Baby…
QWERX helps blockchain cybersecurity by adding robust layers of defense to an already robust distributed ledger technology. Additional layers of QWERX defense:
- Deploy on existing infrastructure. QWERX can be readily deployed via cloud-native technology, is docker-contained and is device-agnostic.
- Real-time alerts. QWERX monitors and provides alerts in real-time. The proactive system allows for faster risk mitigation and prevention.
- Mitigating the human factor. QWERX removes the user from active roles in information security. By removing the user from the security chain, an entire risk ecosystem is dealt with.
- Ephemeral credentials. QWERX uses a multidimensional lookup table created from chaotic data. The system updates the device's handshake every few seconds or even multiple times per second. There are no secret keys to exploit.
Couple those game-changing advantages with the transparency, immutability and decentralization of blockchain cybersecurity and you have one-two-punch knockout power to would-be bad actors against your infrastructure.
Rapidly Evolving Regulatory Landscape
Blockchain transactions can be subject to “money transmission” regulations at the federal, state and even global levels. This would include anti-money laundering (AML) and “know your customer” (KYC) compliance regulations. Violating AML or KYC regulations can carry significant fines and even criminal violations.
According to Coindesk, a glance at current regulatory trends illustrates the point:
- Cryptocurrencies are legal across the European Union but exchange regulations depend on individual member states.
- In the U.K., Australia and New Zealand, national policies governing this sector are still in the development phase.
- Canada and the United States continue to develop regulations to categorize cryptocurrency platforms under well-defined legal brackets.
- At the other extreme, China has drastically tightened its regulations, effectively banning crypto activity in the country.
QWERX helps you stay in compliance despite your region’s level of scrutiny with its Enterprise Secure Perimeter (QESP) console. QESP supports your detailed processes and regulatory needs to keep you in compliance. Furthermore, QWERX is fortified by a team with a strong background in policy management.
QWERX can be your powerful ally as you deploy distributed ledger or blockchain cybersecurity solutions throughout your organization. Its security without secrecy is perfectly matched with blockchain cybersecurity to take its defensive capabilities to the next level — but only if you contact QWERX.
Marty Aquino has been a passionate writer on venture capital, technology, forecasting, risk mitigation, wealth and entrepreneurial topics since 2009. He is the founder of Carbonwolf Energy, a venture-capital firm specializing in world-changing and status-quo-defying technologies and people.
Sources
CBInsights – State Of Blockchain 2021 Report
IBM - What is blockchain security?
CNBC - Crypto hackers steal over $615 million from network that runs popular game Axie Infinity
Chainalysis - $30 Million Seized: How the Cryptocurrency Community Is Making It Difficult for North Korean Hackers To Profit
Coindesk - Crypto AML Compliance: How Risk Scoring Can Help Meet Regulatory Requirements